Many people do not understand the difference between terms such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and other advanced computing concepts. If you are looking for clarification and want to learn why and how these technologies are used in modern cybersecurity solutions, this article will cover:
- The definition of machine learning
- Who uses machine learning and why
- How machine learning works
- The difference between artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Advantages of machine learning and why it is important
- Machine learning and cybersecurity
- The definition of machine intelligence (MI)
- Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud: Advanced Security Pack
What is the definition of machine learning? (ML)
Machine learning (ML) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that can learn from data. Without providing a system with specific instructions, ML can determine patterns, make assessments, and continuously relearn to improve model accuracy and performance using labeled data, algorithms, and statistical models. Data – whether it be text files, images, videos, etc. – is labeled by adding informative tags that identify the context so the ML algorithms can learn from it.
ML develops knowledge and expertise but is limited in how it is applied. For example, if you train a model to recognize cats and dogs, ML cannot learn how to bake a cake because that task is too different from its field of knowledge.

Who uses machine learning and why?
ML uses a variety of algorithms to make decisions, predict outcomes, cluster the results, and detect anomalies. Data clusters are groups of data that have similar characteristics that are not present in other data clusters. Anomaly detection identifies data that are outliers, that is, they are different than data identified in any given cluster.
For example, a ML model will analyze images of dogs and cats and create two clusters – one for dogs and one for cats. If the models analyze an image of a bird, it will detect that this image is an anomaly.
There are countless uses for ML across every industry, including financial services, insurance, healthcare, retail, government, military, agriculture, etc. You experience many examples of ML in everyday life. Examples of how ML is used today include:
- When typing text into your mobile phone or in Microsoft Word, ML is used to recommend words to reduce manual typing and typing errors.
- Search engines use ML to make suggestions when you are looking for specific information or a specific site.
- Email filters use ML to identify spam.
- Banking applications use ML to identify fraudulent transactions and evaluate an individual’s creditworthiness.
- Insurance organizations use ML to identify claim fraud and predict premiums and losses for their policies.
- In healthcare, ML is used for DNA sequencing, to identify disease patterns, detect early-stage health problems, and improve the quality of care.
- In the military, ML is used to improve the accuracy of target identification and the transport of military personnel and equipment.
- Auto manufacturers use ML for image recognition in cars and trucks.
- Netflix uses ML to recommend what you may want to watch next.
- Speech recognition uses ML to identify patterns and finetune the recognition of an individual’s speech.
How does machine learning work?
There are many ways ML can work. Here is one of the simplest examples of ML in action.
Step 0: The business must label and classify data. Data classification is the result of extracting features from the data labels and organizing the data by file type, contents, and other metadata. For example, data can be classified by department, user, confidentiality levels, etc. These types of tasks are accomplished by using supervised ML models that are trained on labeled data.
Step 1: Use the classified data to build the model with training set of data.
Step 2: This step is interlaced with Step 1. The model uses the training set of data to learn. It is an iterative process and includes a feedback loop or error function if something is not properly classified and the error goes back to Step 1 for reclassification. For this process, ML develops a binary decision tree, which is a structure based on a sequential decision process. Starting from the root, the model evaluates a feature and selects one of the two branches. This procedure is repeated until a final leaf is reached.
Step 3: New classified data is now fed into the model for retraining to improve performance and verify accuracy. At this point, the model will identify the percent of false positive results. It is up to the business to decide what percent of false positives is acceptable. If the percent of false positives is unacceptable, the system must be fed more data or extract more features from the data to retrain the model to meet the acceptable false positive level.
Step 4: Optionally, ML can compact or optimize the generated model depending on the algorithm used. For example, it can combine multiple steps or perform parallel processing.
What is the difference between artificial intelligence and machine learning?

AI is the field of science that uses a machine to mimic human intelligence. True AI is not just about a machine having knowledge but also having the machine know how to apply that knowledge using reasoning and deductive logic. There are three AI subsets:
- Narrow AI means that the machine is good at doing one thing, such as playing chess.
- General AI means the machine is good at a few things but is not a cognitive being.
- Super AI can both learn, define its own problems, further learn, and has a sense of self awareness. Skynet, the fictional artificial neural network-based conscious group mind and artificial general superintelligence system in the Terminator series, is an example of super AI.
Fortunately, or unfortunately, we have only achieved narrow AI.
While the objective of AI is to create intelligent machines that can simulate human thinking, ML is a subset of AI that enables machines to learn by themselves using data without being specifically programmed.
Advantages of machine learning technologies and why it is important?
There are significant benefits to ML that include:
- Good for analyzing large data sets. ML can work fast with exceedingly large data sets, something that the human mind is incapable of doing.
- Quickly identifies anomalies and outliers. ML is better at detecting anomalies and outliers because it is not looking for a specific thing – as the human mind does – but is looking for what should not be there.
- Quickly identifies trends and patterns. ML can identify trends and patterns that humans cannot identify, making ML a good application for data mining.
- Continuously improves outcomes. ML does not produce static results but continuously improves its models and outcomes with continuous retraining.
- Automates decision making. With its continuous retraining to improve performance, ML is good at quickly automating decisions. For example, ML can analyze your online behavior and recommend appropriate websites, products, or services that you may want. ML is an especially important component for improving the customer experience (CX).
Popular methods of machine learning
Within the field of ML, there are different types of learning:
- Supervised learning uses labeled data to train (or supervise) the model and accurately predict outcomes. Using labeled data, the model relearns over time to improve predictions and performance.
- Unsupervised learning uses a family of techniques to analyze, cluster, discover patterns, and label data without human intervention (unsupervised).
- Semi-supervised learning uses both labeled and unlabeled data. Typically, it uses a small amount of labeled data and large data sets of unlabeled data. Speech analysis and text documents both have a large volume unlabeled data – audio files, books, scripts, blogs, etc. –all of which can be time consuming and costly to manually label. With just a small volume of labeled data, semi-supervised learning can extract the relevant features.
- Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning that allows a system to learn by trial and error – using a feedback loop – to adapt its strategy after each decision step. The goal of the algorithm is to find a balanced solution that will maximize its rewards. Reinforcement learning is often used in gaming apps.
Machine learning and cybersecurity
Next generation, advanced cybersecurity solutions use ML for a variety of tasks. Some examples include:
- Classifying files into malware and clean files
- Identifying phishing and spam emails
- Identifying anomalies when a user logs onto a system by analyzing and comparing time of day and user locations. For example, if a user typically logs on between 8 a.m. and 5 p.m. from New York and the system sees that this user ID logs on at 2 a.m. from China, this could be an attack.
By focusing on tasks such as these, ML can significantly improve data security because it can quickly analyze large amounts of data at scale and identify anomalies and potential attacks faster than humans can. This speed helps stop attacks faster and can reduce the time between when an attack happens and when a business realizes that an attack has happened.
So then, what is machine intelligence?
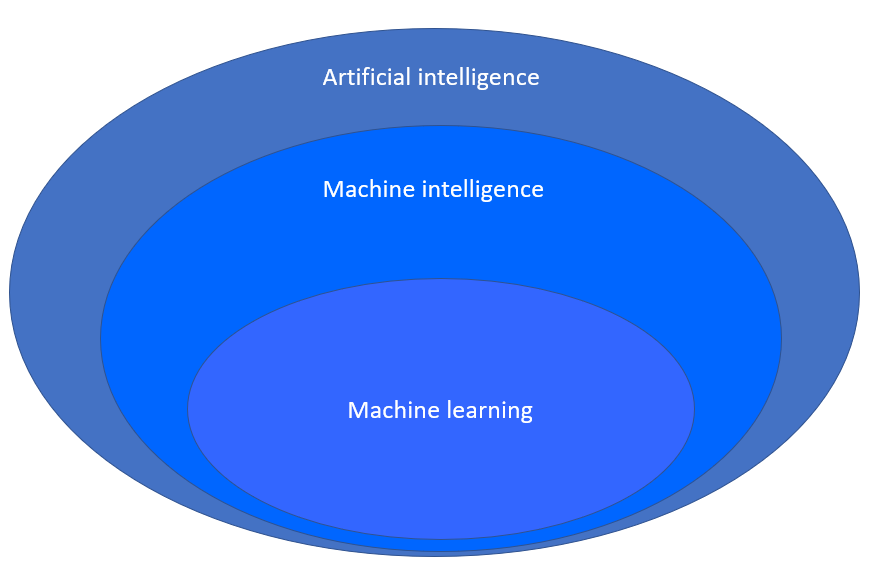
Machine intelligence (MI) is a superset of ML and is a relatively new term. MI interacts and learns more from multiple inputs – which are not yet defined – and the environment, and can process and adapt new inputs using the classical feedback loop or regression testing (where it learns from its mistakes).
According to Forbes, machine intelligence is “what is created when machines are programmed with some (but not all) aspects of human intelligence, including learning, problem solving, and prioritization.
“Machine intelligence will have a suite of different machine learning methods available to it, as well as a battery of automation techniques, and will smartly prioritize and deploy a sequence of them in the right order, with the right timing to achieve specific business goals. You can think of machine intelligence as a higher evolution of machine learning with prioritization and goals added in – a steppingstone on the path to true AI.” Source: Forbes. (2019) What exactly is machine intelligence?
For example, a system can have multiple machine learning algorithms:
- One algorithm classifies emails based on the text contained within each email.
- Another algorithm detects any URLs inside the email and looks for malicious links.
- A third algorithm analyzes any images contained in the email using image recognition.
Independently, each of these are ML but when assembled and prioritized to work together in the right order, you have machine intelligence.
Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud – Advanced Security
Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud is the only solution enhanced by machine intelligence that natively integrates cybersecurity, data protection, and management to protect endpoints, systems, and data. This synergy eliminates complexity, so service providers can protect clients better while keeping costs down. It provides:
- The industry’s best backup and recovery with full-image and file-level backup and recovery to safeguard workloads on more than 20 platforms – with near-zero RPOs and RTOs.
- Essential cyber protection at no additional cost with an advanced MI-based behavioral detection engine that stops malware, ransomware, and zero-day attacks on your client’s endpoints and systems.
- Protection management that is built for MSPs to enable thorough post-incident investigations and proper remediation, while keeping costs down by collecting digital evidence and storing it in a secure central repository.
The Advanced Security pack is an add-on to Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud that enables MSPs to extend their security offering with:
- Full-stack, real-time anti-malware protection covering all attack vectors with multiple defense layers
- URL filtering to block malicious URLs, web-based attacks, and COVID-19 scams
- Exploit prevention using behavior-based detection heuristics to prevent the exploitation of unknown vulnerabilities, including memory exploits and injections
- Anti-malware scans of data in the Acronis Cloud to offload the impact to client endpoints, enable more aggressive scans, and ensure malware-free backups
- Forensics data in backups so to collect digital evidence faster and reduce the cost of remediation
- CPOC threat feed to increase reactiveness to emerging threats and get remediation suggestions
- Automatic allowlisting to reduce false positives and enable more aggressive scanning
- Malware reinfection prevention that scans for malware and updates AV definitions during recovery to prevent a threat from reoccurring
Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud with Advanced Security enables service providers to offer more cybersecurity services to clients while reducing the management burden, replacing non-integrated antivirus tools with complete endpoint security that’s integrated with data protection.
About Acronis
A Swiss company founded in Singapore in 2003, Acronis has 15 offices worldwide and employees in 50+ countries. Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud is available in 26 languages in 150 countries and is used by over 21,000 service providers to protect over 750,000 businesses.



